

So if a distant galaxy emits a characteristic spectral line of 91 nm ( ultraviolet light at the 'Lyman limit') but when observed on Earth it appears to be 640 nm (red) we can calculate the red shift using this equation: Redshift Astronomers determined the Universe is expanding based on the color of light emitted from galaxies and stars just like the doppler effect. The following equation is used to calculate redshift: This is because galaxies are receding (moving away) at such high speeds that relativistic effects need to be considered in calculations. The Doppler equation used for sound calculations cannot be used in this situation.
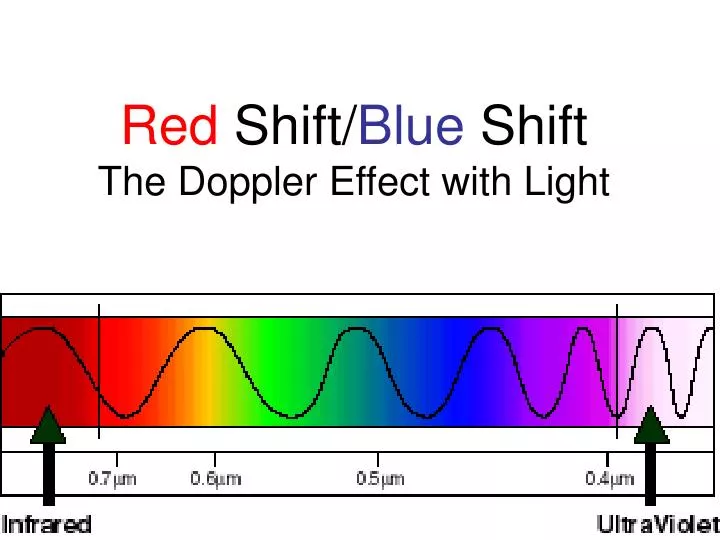
Redshift is also the name of the factor z indicating the relative change in wavelength due to the Doppler shift for a receding galaxy. The upper diagram shows the absorption spectrum from a stationary galaxy with one wavelength of light and no redshift. Lower diagram shows spectrum of light redshifted from a distant galaxy moving away from the Earth
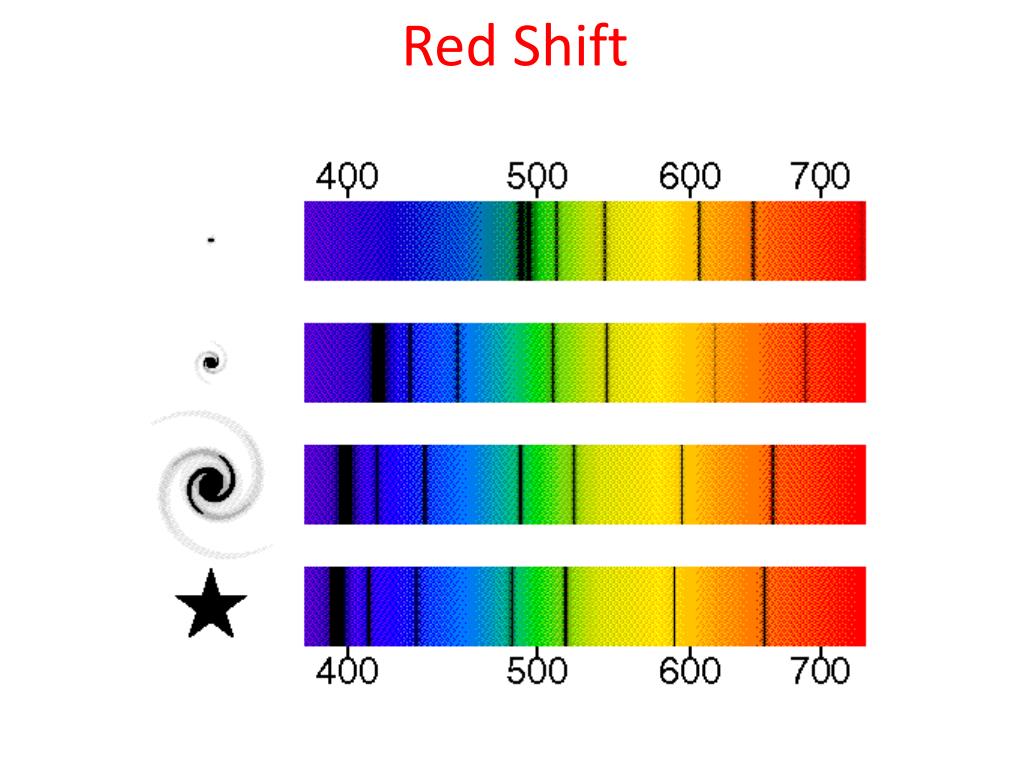
This indicated the stars were moving away from Earth (just as the sound of a siren moving away from you has a decreased frequency and increased wavelength).Īs the light was shifted towards the red end of the spectrum (lower frequency/longer wavelength) this phenomenon was termed 'redshift'. If the frequency has decreased, the wavelength must also have increased.The same shifts in frequency and wavelength are also observed for light coming from stars in distant galaxies.īy comparing the light from distant stars with the spectrum of light from our Sun it was noticed that the spectra from distant stars had a slightly decreased frequency and slightly increased wavelength. Light from these galaxies is shifted to longer (and this means redder) wavelengths - in other words, it is red-shifted. This means the frequency of the sound is decreasing. As the motorbike moves away from you the pitch of the sound will become lower. Using the results from the nearer ones, it. There are 3 types of redshifts: Doppler shift. This shift is apparently a Doppler shift and indicates that essentially all of the galaxies are moving away from us. To help you to remember what happens to the wavelength and the frequency of an object as it moves further away, it is useful to think about how the sound of a motorbike would change as it travels past and then away from you. If the observed wavelength is more, then the phenomenon is known as redshift. You need to know that in the visible light spectrum red light has the longest wavelength and the smallest frequency. The observer in front observes a blue shift, the observer behind observes a red shift Some Examples of Strong Red Shifting Include: A gamma ray perceived as an X-ray, visible light perceived as radio waves are seen in spectroscopic observations. Light from a star that is moving towards an observer will be blueshifted and light from a star moving away from an observer will be redshifted This is known as redshift as the light moves towards the red end of the spectrum.If an object moves away from an observer the wavelength of light increases.This is known as blueshift as the light moves towards the blue end of the spectrum.

If an object moves towards an observer the wavelength of light decreases.This effect is known as the Doppler effect.The wavelength behind the source increases (λ + Δλ) and the frequency decreases The following is an example of the Doppler effect: as one approaches a blowing horn, the perceived pitch is higher until the horn is reached and then becomes lower as the horn is passed.The wavelength of the waves in front of the source decreases (λ – Δλ) and the frequency increases.A moving object will cause the wavelength, λ, (and frequency) of the waves to change:.If the wave source moves, the waves can become squashed together or stretched outĭiagram showing the wavefronts produced from a stationary object and a moving object But after increasing the concentration of EDTA beyond 100mM, there is a peak shift in the sample which is bi-directional- one apex peak is at 313 nm and other at 344 nm.Usually, when an object emits waves, the wavefronts spread out symmetrically.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
